A Holistic Approach To Obesity

Obesity refers to a condition in which an individual has an excessive amount of body fat. It’s not only a cosmetic concern but also increases the risk of health problems, especially chronic diseases such as diabetes, cancer, and cardiovascular diseases. The method used to determine if someone is obese/overweight is the body mass index (BMI) dividing the weight in kilograms by the square of the height in meters (kg/m2).
BMI categories
Underweight=<18.5
Normal weight=18.5–24.9
Overweight=25–29.9
Obesity (class 1)=30.0-34.9
Obesity (class 2)=35.0-39.9
Extreme obesity (Class 3)= 40.0 and higher
(in the case of children, age also has to be taken into consideration due to their growth development.)
Causes/risk factors
There are many causes/risk factors for obesity, ranging from genetic (e.g. Prader-Willi syndrome, Cushing syndrome), behavioural and hormonal influences (e.g. hypothyroidism), certain medication (e.g. anti-depressants, anti-seizure medication, anti-psychotic medications, steroids, contraceptive pills), pregnancy, quitting smoking, lack of sleep, etc. However, even if these risk factors are present, this doesn’t mean that you become obese because most of these factors can be counteracted by means of a healthy diet and physical exercise. In general, the main cause of obesity is inactivity and unhealthy diet/eating habits. If you consume more calories than the body burns, your body stores the excess calories as fat.
Health risks
With obesity you have an increased risk of developing the following health problems:
- breathing disorders (sleep apnea, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), exacerbation of asthma, aspiration pneumonia, obesity hypoventilation syndrome)
- cardiovascular diseases (coronary artery disease (CAD), hypertension, atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, stroke)
- depression
- high blood cholesterol (increased LDL, low HDL)
- osteoarthritis
- metabolic syndrome (increased blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat around the waist, abnormal cholesterol/triglyceride levels)
- urinary incontinence
- type 2 diabetes
- gallbladder and liver diseases (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD))
- some types of cancer
- gynecological problems (infertility, irregular periods)
- erectile dysfunction and sexual health issues
Epidemiology
Obesity has been considered a problem prevailing in more developed countries, but obesity is also drastically in underdeveloped countries (rural areas). According to a report published earlier this year by the Institute of Health Metrics and Evaluation based at the University of Washington in Seattle, more than 603 million adults and 107 million children (out of a global population of around 7.5 billion) are obese. That represents around 5% of all children and 12% of all adults. In India, 31% of men and 29% of women are overweight – a trend which has grown over the last 11 years.1
A holistic approach to obesity
Besides conventional therapies for weight loss (diet, physical exercise, prescription medication, bariatric surgery) whereby weight control often cannot be achieved2, I suggest alternative/complementary ways of dealing with obesity and its symptoms: Yoga, Ayurveda, and Acupuncture.
Yoga
Asanas (postures) and pranayama (breathing exercises) are a great way to deal with daily stressful situations, calming down the mind, and increasing the blood supply to different organs, expelling toxins from the body, bringing balance, and also to control body weight.
Here’s a list of some of the beneficial asanas and pranayamas to lose weight:
Surya Namaskar
Sun salutation – preferably in the morning: 12 sets (1 round=12 poses, 1 set=2 rounds). This is a full body workout uniting the body, mind, and breathing where you burn up to 400 calories in just 30min. It strengthens and stretches all the major muscle groups, lubricates the joints, massages internal organs, and increases blood circulation.

Bhastrika
Bellows breath: sit in Sukhasana (crossed leg), inhale and exhale normally a few times, then inhale and exhale repeatedly, fully and deeply contracting the diaphragmatic muscles; when inhaling blow air into the stomach, and when exhaling expel the air. Do this in a rhythmic manner, for 3 rounds (10 times=1 round), maintain the speed and normal breathing in-between. You will strengthen your heart and lungs, improve your digestion, tone your abdominal region, and calm your mind.
Kapalbhati
The cleansing breath: sit in Sukhasana, inhale passively and exhale sharply through the nose while using the muscles of the throat and abdomen (place your hand on the abdomen to feel the contractions). Practise 3-5 rounds (10 times=1 round) and breathe normally in-between. This has an awesome cleansing effect and burns belly fat.
Nadi Shodana
Alternate nostril breathing: sit in Sukhasana, close the left nostril with your thumb, and breathe in for 2 seconds from the right nostril, close the right with the middle finger, and hold your breath for 4 sec. Release your thumb from your left nostril, exhale for 2 seconds, inhale from the left for 2 sec, hold for 4 sec, and exhale from the right for 2 sec. Inhale right and practice 5 rounds. Normal breathing in-between. This balances the opposite energies in our system, balances hormones, releases toxins, and calms the mind.
Ayurveda
The Ancient Indian medical system, meaning “Science of Life”, focuses greatly on a healthy way of living and on our digestion. Due to wrong eating habits, our body produces toxins leading to more problems. According to Ayurveda, obesity is an imbalance of the system mainly caused by an irregular lifestyle.
The recommended treatment is diet and lifestyle modifications:
- mindful eating
- chew 32 times
- walk 100 steps after eating
- don’t eat when angry, stressed or sad
- eat at regular times
- don’t snack
- eat after emptying your bowels
- consume fresh and seasonal fruits/vegetables
- eat warm and fresh food
- don’t consume incompatible food
- early, light dinner
- good night’s sleep
- exercise daily.
Panchakarma: Purification process of the body
Udwartana: dry powder massage with chickpeas flour, barley and triphala (ayurvedic medicine) and internal medication (herbs) if needed.
Additionally, drinking lukewarm water 30 minutes before meals helps in eating less while drinking lukewarm water with honey and lemon juice can help to burn fat.
Watch this interview with three renowned Ayurvedic doctors of the Gujarat Ayuveda University in Jamnagar, Gujarat, India to learn more about Panchkarma:

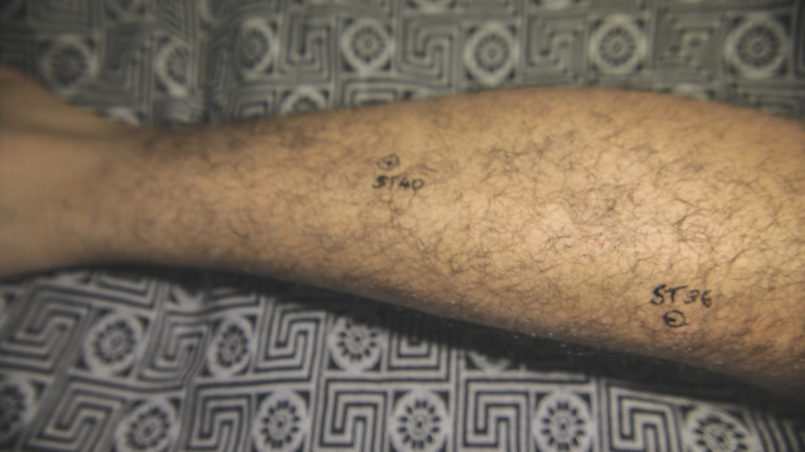
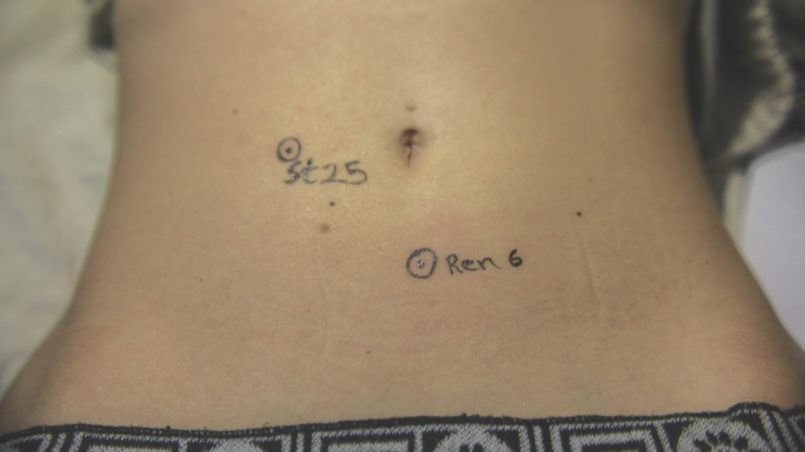
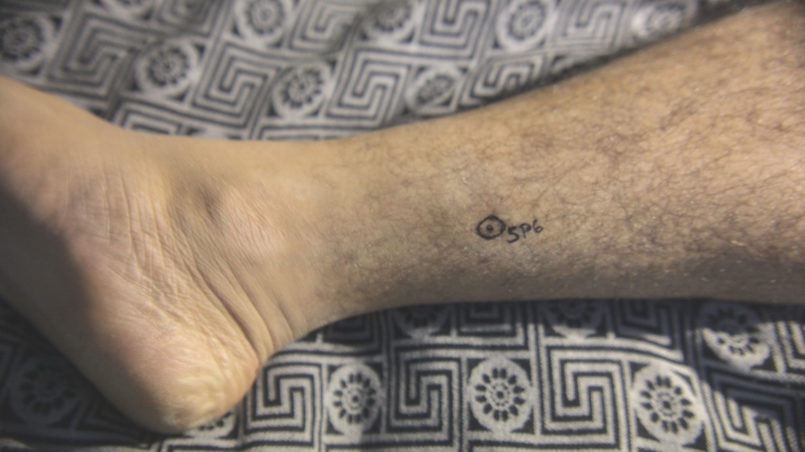
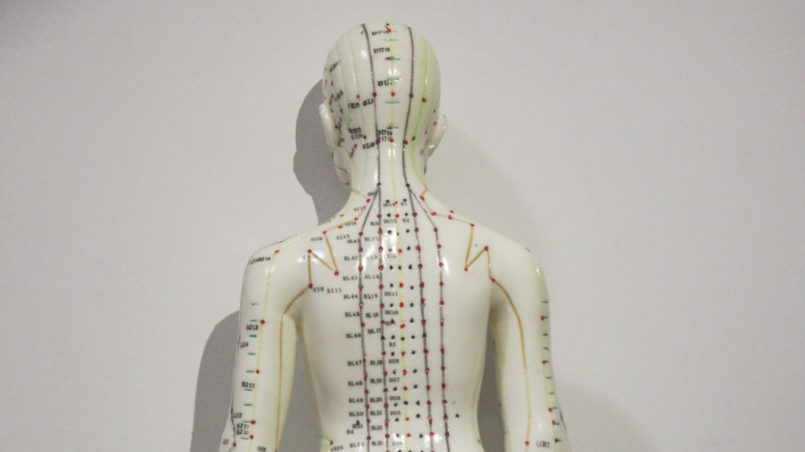
Acupuncture or Acupressure
Acupuncture and Acupressure, as part of TCM (Traditional Chinese Medicine), work by inserting needles or applying gentle pressure to points situated on 12 different meridians, carrying “qi”/”chi” (energy) in our body. According to TCM, a blockage of energy leads to illness. Hence acupuncture helps to unblock and allows an easy flow of qi. Regarding weight loss, as explained by the International Acupuncture Training Centre in Beijing (China), different points which act on the digestive system, water metabolism, toxins’ removal, hunger and satiety centre of our brain, blood circulation, and relaxation can be stimulated, but the treatment plan always depends on the cause of the obesity and on the patient’s overall health condition.
Some of these points are:
For more information, please consult a doctor, a yoga or Ayurvedic practitioner, or an acupuncturist.
_
1 https://www.telegraph.co.uk/travel/maps-and-graphics/the-most-obese-fattest-countries-in-the-world/, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27546800
2 https://aim.bmj.com/content/31/1/88)